Trump’s New NASA Budget Proposal Cuts Deep: The Trump FY2026 NASA budget proposal has ignited intense debate among scientists, engineers, educators, and policymakers. With a dramatic shift in priorities, the proposed budget slashes NASA’s funding for space science, Earth observation, and flagship robotic missions—while giving a modest boost to crewed exploration efforts to the Moon and Mars. Critics call the changes “draconian,” with concerns ranging from job loss and national security risks to a possible loss of American leadership in global space exploration. For students, researchers, and professionals, this proposal represents a pivotal moment in the future of U.S. science and space leadership.
Trump’s New NASA Budget Proposal Cuts Deep
The Trump administration’s 2026 NASA budget proposal is more than a line item—it’s a bold redefinition of American priorities in space. It cuts deeply into research, discovery, and innovation that serve not just scientific curiosity, but real-world applications in weather, climate, and national defense. While Artemis and Mars missions survive, they do so at the cost of a diverse and balanced space portfolio. This moment demands engagement—from scientists and citizens alike. The decisions made this year will ripple across generations.
| Category | Summary |
|---|---|
| Total NASA Budget | From $24.8 billion (FY2025) to $18.8 billion (FY2026), a 24% drop |
| Science Budget Cut | Halved from $7.8 billion to $3.9 billion |
| Human Exploration | Modest increase from $7.7 billion to $8.5 billion |
| Programs Canceled | Mars Sample Return, Chandra X-ray Observatory, Roman Telescope, Venus missions, Earth satellites |
| Job Impact | Up to 5,500 NASA employees affected; up to 14,000 indirect jobs at risk nationwide |
| State Impact | California, Texas, Maryland hit hardest |
| Industry Fallout | Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Boeing, and JPL among affected contractors |
| Official Budget Resource | NASA Budget Portal |
What’s in the Trump’s New NASA Budget Proposal Cuts Deep?
The Trump administration’s 2026 budget blueprint proposes reducing NASA’s funding by over 24%, bringing the agency’s total funding down to $18.8 billion. This would be the lowest budget since FY2009 when adjusted for inflation.
The key shift is clear: science is out, and human exploration is in. The budget proposes:
- Ending or sharply reducing funding for over 40 science missions.
- Increasing investment in the Artemis program, including lunar landing systems and infrastructure.
- Funding early development of Mars crewed mission technologies.
- Curtailing Earth-observing missions used to track climate change, ocean health, and natural disasters.
NASA insiders say this kind of budget reallocation would lead to “organizational trauma” and irreversible damage to long-planned missions that are already in advanced stages.
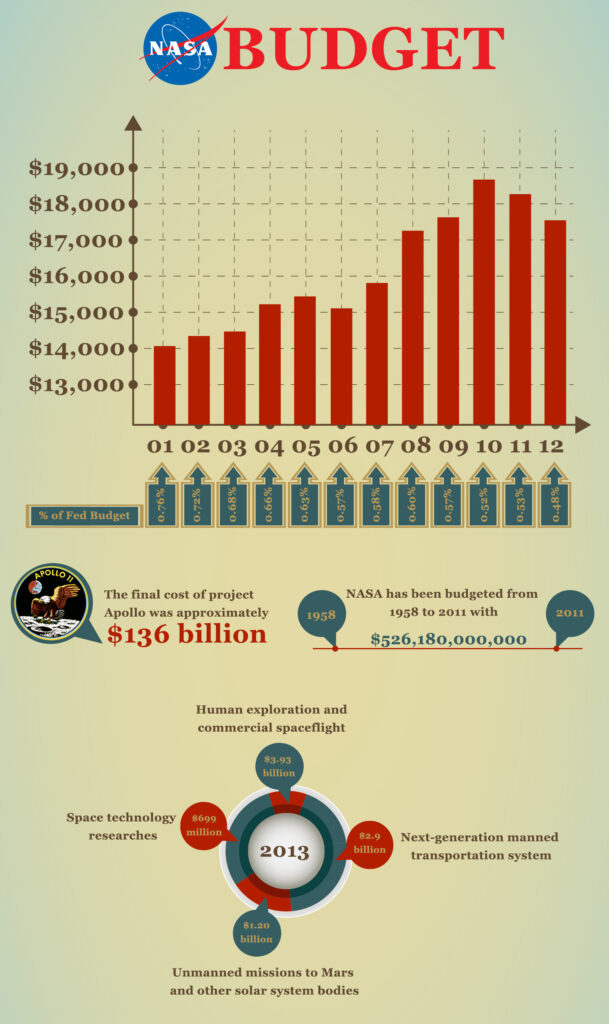
A Timeline: NASA Funding in Historical Context
To understand the gravity of the proposed budget, here’s a look at NASA funding over time:
| Year | Budget (in billions) | Notable Events |
|---|---|---|
| 1966 | $5.9B (4.4% of federal budget) | Apollo peak |
| 1986 | $8.8B | Challenger disaster |
| 2004 | $15.4B | Bush’s Moon-to-Mars Vision for Space Exploration |
| 2010 | $18.7B | Obama cancels Constellation Program |
| 2020 | $22.6B | Artemis ramp-up under Trump |
| 2025 | $24.8B | Highest science budget in NASA history |
| 2026 (proposed) | $18.8B | Largest cut to science missions since 1981 |
This would represent the largest percentage cut to NASA’s science division in over three decades.
Canceled and Defunded Programs
Let’s take a closer look at the science missions that would be directly impacted or canceled under the Trump FY2026 proposal:
Mars Sample Return Mission
This high-priority, international mission aimed to bring samples collected by the Perseverance rover back to Earth. More than $7 billion has already been invested. Canceling it would strand invaluable geological and possibly biological samples on the Martian surface indefinitely.
Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
Planned as a next-gen observatory to succeed Hubble, Roman was slated to explore dark energy, exoplanets, and the early universe. The project is already in advanced stages of assembly, yet would be abruptly terminated.
Chandra X-ray Observatory
Operational since 1999, Chandra has been instrumental in observing black holes, galaxy clusters, and cosmic phenomena. Eliminating funding would end the mission prematurely, despite its scientific productivity and longevity.
VERITAS and DAVINCI+ (Venus Missions)
These long-awaited missions to explore Venus’s atmosphere and geology—originally selected through competitive peer review—would be shelved indefinitely.
Earth Science Missions
Several missions key to understanding our changing climate are targeted for reduction or cancellation, including:
- PACE (Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem)
- GeoCarb (greenhouse gas tracking)
- CLARREO Pathfinder (climate monitoring from orbit)
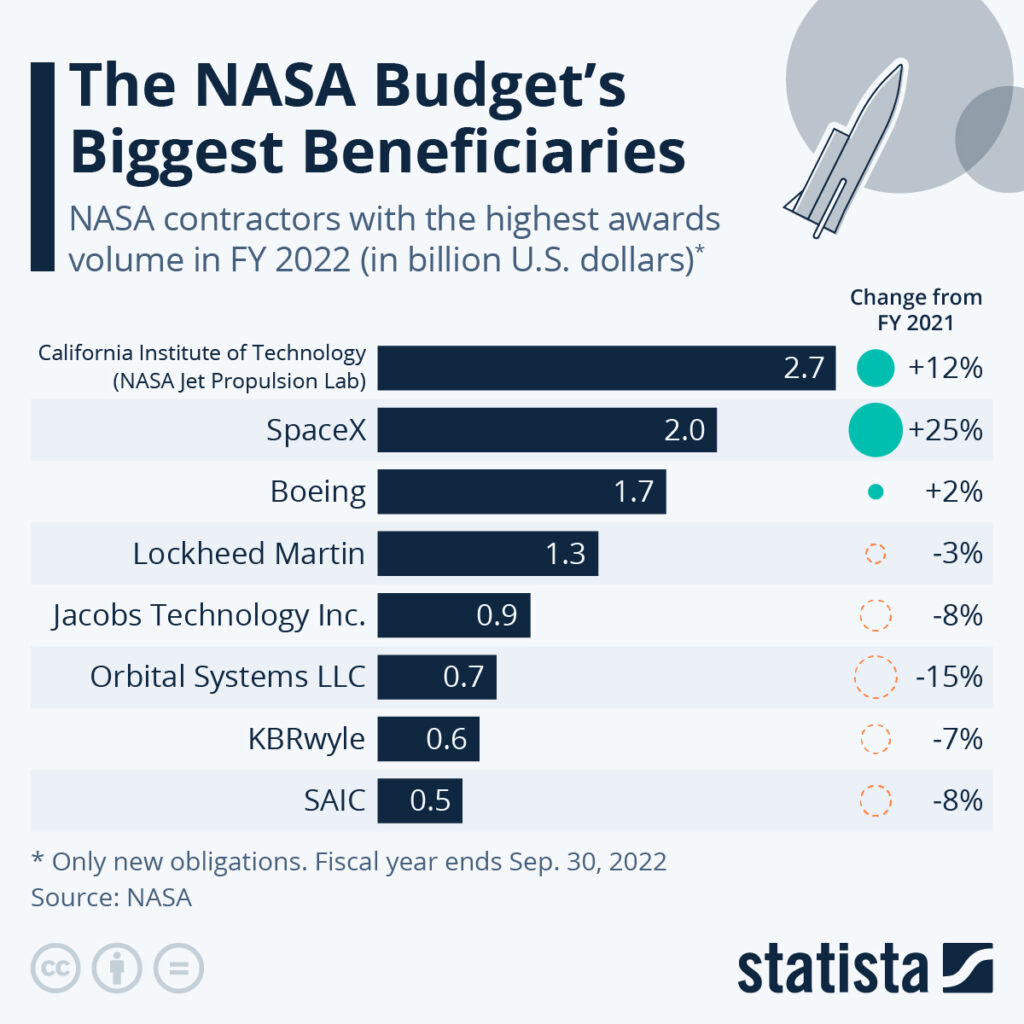
National and Local Impacts
The proposed NASA cuts would ripple through state economies, federal research facilities, and private aerospace companies. Here’s where the pain would be felt most:
California
- Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) could lose dozens of active and planned missions.
- Up to 14,000 jobs (direct and indirect) could be at risk.
- Over $1.4 billion in potential economic impact.
Texas
- Home to the Johnson Space Center. Human spaceflight teams are partially protected, but mission operations and engineering support may be affected.
- Houston’s space economy could see layoffs in support and supplier roles.
Maryland
- NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, focused on Earth science and satellite missions, faces major reductions.
- Cuts could affect contractors, educational outreach, and research institutions in the region.
Impact on the Space Industry
The effects extend beyond NASA. The U.S. commercial space sector depends heavily on NASA contracts and partnerships. Companies likely to experience cascading effects include:
- Lockheed Martin – primary contractor on Mars Sample Return and Orion capsule.
- Northrop Grumman – involved in telescope instrumentation and satellite development.
- Boeing – heavily invested in the Space Launch System (SLS), also under review.
- Sierra Space, Blue Origin, SpaceX – could see shifts in priorities or funding for lunar infrastructure.
The risk to America’s industrial base is significant, with potential supply chain disruptions, delayed contracts, and a loss of high-skilled labor.

Policy and Political Reactions
While budget proposals are ultimately controlled by Congress, the Trump administration’s document has prompted immediate bipartisan concern.
- Senator Ted Cruz (R-TX): “We must preserve our investments in Artemis and science. I’ll work with colleagues to protect critical missions.”
- Representative Don Beyer (D-VA): “The proposed budget would devastate American science. We will fight to restore it.”
- The Planetary Society: “This is an extinction-level threat to science at NASA.”
Congressional hearings have already begun, and budget negotiations will continue through the summer. Amendments and funding restorations are expected, but the battle is far from over.
What Students, Educators, and STEM Professionals Need to Know
The uncertainty caused by these cuts affects students, early-career professionals, and educational institutions across the country.
For Students:
- Stay flexible. Consider alternate paths in climate science, AI, data science, and commercial space roles.
- Seek out internships through NASA’s STEM Engagement Office.
- Take advantage of online courses on platforms like Khan Academy, Coursera, and edX.
For Educators:
- Use this budget proposal as a teaching moment. Discuss civics, science policy, and how budgets shape national priorities.
- Support programs that build resilience: robotics clubs, maker spaces, coding bootcamps, and space camp scholarships.
For Professionals:
- Look for opportunities with international space agencies, NOAA, or private companies.
- Join advocacy groups like The Planetary Society to stay engaged and informed.
- Network at conferences like AGU, AIAA, and AAAS.
It’s Official: NASA Just Confirmed What the Oceans Really Look Like from Space
NASA Just Discovered Solar Curtains on the Sun—Here’s How This Plasma Spectacle Forms











