
Claiming Social Security at 62 vs 70: When it comes to retirement planning, one of the most important decisions you’ll face is when to start collecting your Social Security benefits. Many people ask, “Should I claim Social Security at 62 or wait until 70?” The decision can significantly impact your monthly income and overall financial security in retirement. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the pros and cons of claiming Social Security at 62, 67 (Full Retirement Age or FRA), and 70. We’ll break it down so it’s easy to understand, regardless of your age or financial expertise. Whether you’re approaching retirement, in your 40s starting to plan, or just curious about your options, this article will give you all the tools you need to make an informed choice.
Claiming Social Security at 62 vs 70
Deciding when to claim Social Security is a big decision that can affect your retirement income for the rest of your life. Whether you choose to claim at 62, 67, or 70, it’s important to carefully evaluate your personal situation—consider your health, work situation, other retirement savings, and long-term goals.
If you can afford to wait, delaying your benefits until age 70 will maximize your monthly benefits and give you financial security in the long run. However, if you need the money sooner, or if you have health concerns, claiming at 62 could be a better option. Take the time to research your options and consult with a financial planner if you need help making the right choice. The right strategy will depend on your unique situation, but knowing your options will ensure you make the best decision for your future.
| Claiming Age | Percentage of Full Benefit | Monthly Example | Annual Example | Benefits of Waiting | Impact of Claiming Early |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | 70% | $1,400 | $16,800 | Lower monthly payments | Immediate access to funds |
| 67 (FRA) | 100% | $2,000 | $24,000 | No penalty | No penalty but limited funds |
| 70 | 124% | $2,480 | $29,760 | Highest payout | Delayed access to funds |
What is Social Security?
Before diving into the timing of when to claim, let’s review what Social Security is and how it works. Social Security is a government program designed to provide income to people who are retired, disabled, or survivors of deceased workers. It’s based on your earnings record—essentially, how much you’ve worked and contributed to Social Security over your lifetime.
Your Full Retirement Age (FRA) is the age at which you’re eligible to receive your full benefits without any reductions. The FRA varies depending on your birth year, but it’s usually between 66 and 67. If you claim before your FRA, you’ll face a reduction in benefits. If you wait past your FRA, your benefits will increase by up to 8% per year until you reach age 70.
Understanding these key points will help guide your decision. So, let’s explore how claiming at different ages impacts your benefits.

Claiming Social Security at Age 62: Early Access, But at a Cost
Claiming Social Security benefits at age 62 is the earliest you can begin receiving payments, but it comes with significant trade-offs. Many people find this appealing because it gives them immediate access to income. Let’s explore the reasons why some people choose to claim early—and the downsides of doing so.
Advantages of Claiming at 62:
- Immediate Access to Income: One of the main reasons people claim early is to get income sooner. If you need the money—perhaps because you’re unable to work, have health issues, or need to cover living expenses—Social Security at 62 can help fill that gap.
- Shorter Life Expectancy: If you have health concerns or a family history of early mortality, claiming earlier may give you more benefit in the years you do live.
- Retirement Flexibility: If you want to retire earlier than expected, claiming Social Security at 62 might be your best option. It allows you to leave the workforce while still receiving benefits.
Disadvantages of Claiming at 62:
- Reduced Monthly Benefits: The biggest downside to claiming at 62 is that your monthly payment is reduced by up to 30% compared to what you would get at your FRA. This reduction is permanent, meaning you’ll receive less for the rest of your life. For example, if your monthly benefit at your FRA is $2,000, you’ll only receive $1,400 if you claim at 62. That’s a $600 difference each month.
- Earnings Limit: If you claim benefits and continue to work before reaching your FRA, the SSA will reduce your benefits if your earnings exceed certain limits. For example, if you earn more than $21,240 annually in 2025, Social Security will withhold $1 for every $2 you earn above that limit. Example: If you’re earning $30,000 a year, you could lose $4,380 in benefits for that year.
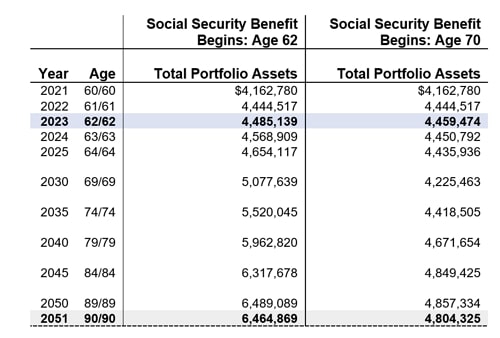
Claiming Social Security at Age 70: Maximize Your Benefits
While claiming at 62 is an option, waiting until 70 can result in the highest possible monthly benefits. Here’s why many financial experts recommend waiting as long as you can.
Why Waiting Until 70 is Beneficial:
- Larger Monthly Benefits: By delaying your benefits until age 70, you earn an 8% annual increase in your benefit for every year you wait past FRA. So, if your FRA benefit is $2,000, waiting until 70 will increase it to $2,480. That’s an additional $480 every month for the rest of your life.
- Better Long-Term Financial Security: If you live past the break-even point (usually around age 80), waiting to claim can give you significantly more in benefits over the long run. While you won’t get benefits in your 60s, the larger checks in your 70s and beyond often more than make up for it.
- Spousal and Survivor Benefits: If you’re married, waiting to claim can also benefit your spouse. When one spouse delays until 70, the other spouse may receive a higher survivor benefit if the higher earner passes away. This can be a key part of a retirement planning strategy.
Disadvantages of Waiting Until 70:
- Delayed Access to Income: The most obvious downside of waiting is that you won’t have any income from Social Security until you turn 70. This could be a major consideration if you need income immediately or have insufficient retirement savings.
- No Retroactive Payments: The SSA does not provide retroactive payments. In other words, if you delay claiming past your FRA, you won’t be given a lump sum for the months or years you could have been collecting. You will only receive payments based on your age at the time you apply.
When Should You Claim Social Security: Claiming Social Security at 62 vs 70
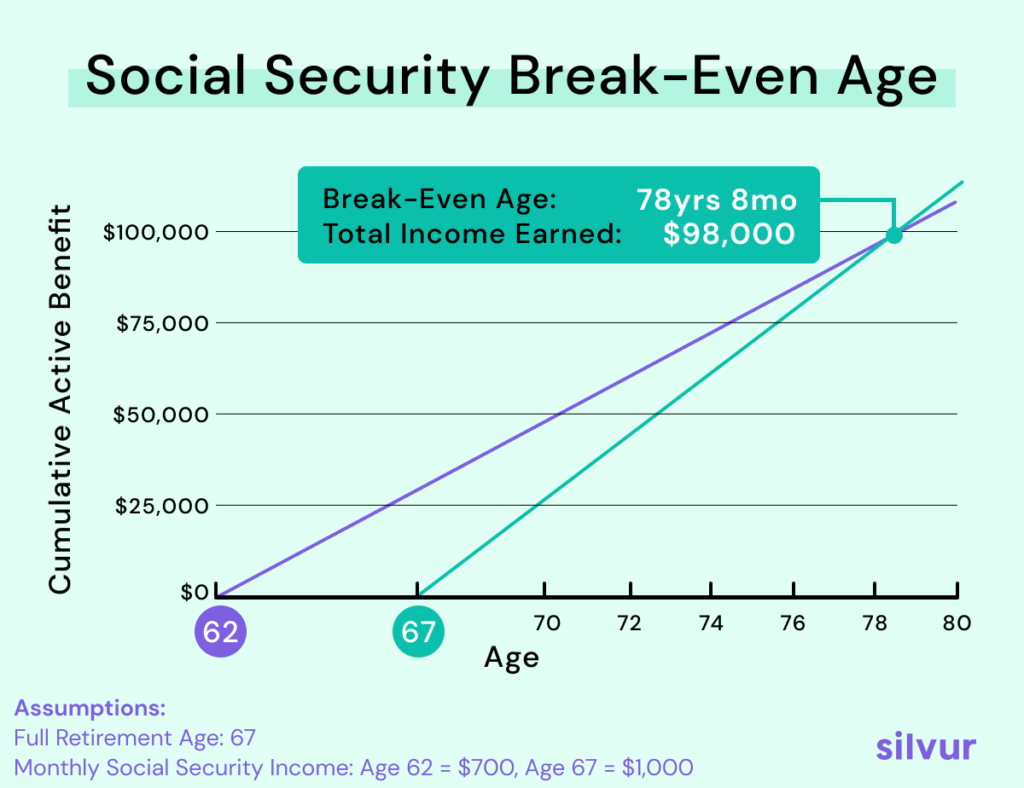
The decision to claim Social Security depends on your personal circumstances, such as your health, financial needs, retirement plans, and life expectancy. Here’s how to strategically think through your options:
1. Health and Life Expectancy:
If you expect to live a long life, delaying Social Security until 70 can maximize your benefits. On the other hand, if your life expectancy is shorter due to health reasons or family history, you may want to claim earlier to get the maximum benefit in your lifetime.
2. Financial Needs:
If you don’t have other sources of income and need money to live on, claiming at 62 could be necessary. However, if you have retirement savings, a pension, or other investments, waiting until 70 might be the best way to maximize your Social Security benefits.
3. Spousal Considerations:
Married couples can benefit from coordinating their Social Security strategies. For example, one spouse can claim early while the other delays benefits to age 70. This helps ensure both spouses maximize their lifetime benefits.
4. Other Retirement Savings:
If you have a strong retirement portfolio (such as a 401(k) or IRA), you may not need to claim Social Security early. Delaying benefits could allow you to grow your nest egg for a longer, more secure retirement.
Full Retirement Age Is Changing Again – What It Means for Your Social Security Benefits
Social Security Faces Collapse by 2034—Retirees Beware of Major Cuts to Your Benefits
Big Changes to Social Security in 2025: Who Can Still Claim Full Retirement Benefits?











